Matching
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | Anti-Federalists | b. | boycott | c. | Commerce and Slave
Trade Compromise | d. | Connecticut Compromise | e. | English Bill of Rights | f. | Federalists | g. | Magna Carta | h. | separación de
poderes | i. | representative government | j. | Virginia Plan | k. | Petition of
Right | l. | charter colonies | m. | Articles of Confederation | n. | proprietary
colonies |
|
|
|
1.
|
called for representation in Congress by population or by the amount of money
given to the central government
|
|
|
2.
|
idea that government should serve the will of the people
|
|
|
3.
|
agreement that, in Congress, States be represented equally in the Senate and by
population in the House
|
|
|
4.
|
those for whom the Constitution represented a too-powerful central
government
|
|
|
5.
|
first English charter of liberties which included such fundamental rights as
trial by jury and due process of law
|
|
|
6.
|
organized action to change opponents' behavior by refusing to buy or sell
their goods
|
|
|
7.
|
statement that Parliament forced the king to sign, declaring that even a
monarch must obey the law of the land
|
|
|
8.
|
organized by people to whom the king had made a grant of land available and
could be settled and governed in whatever manner they saw fit
|
|
|
INTERPRETING CHARTSThe events leading up to the American
Revolution and Constitutional Convention can be seen as a series of causes and effects. Complete the
chart below by filling in each box with the letter of the correct term from the list on the right.
The first one is done for you. You will not use all the terms.
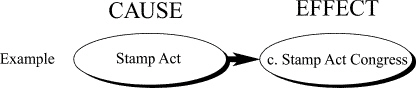 a. | Intolerable Acts | b. | need for strong central
government | c. | Stamp Act Congress | d. | creation of army, money system,
treaties |
|
|
|
9.
|
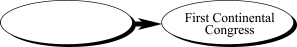
|
|
|
10.
|
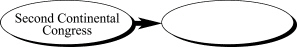
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
MAIN IDEAS
|
|
|
11.
|
In the charter colonies, most governmental matters were handled by
a. | the British monarch. | b. | Parliament. | c. | a
proprietor. | d. | the colonists. |
|
|
|
12.
|
Which idea is NOT included in the Declaration of Independence?
a. | People have certain natural rights. | b. | God gives certain people the right to
govern. | c. | Government can exist only with the people's permission. | d. | The people may
change or abolish the government. |
|
|
|
13.
|
All of the following influenced the Framers in developing the Constitution
EXCEPT
a. | State constitutions. | b. | John Locke's Two Treatises of
Government. | c. | Virginia's royal charter. | d. | British
tradition. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which colony was founded mainly as a place for personal and religious
freedom?
a. | Virginia | b. | Georgia | c. | Massachusetts | d. | New York |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which feature did the State constitutions and the Articles of Confederation have
in common?
a. | royal governors | b. | bill of rights | c. | principle of popular
sovereignty | d. | a strong executive elected by popular vote |
|
|
|
16.
|
Which of these State constitutions is the oldest and still in force
today?
a. | Massachusetts | b. | South Carolina | c. | New
Hampshire | d. | Virginia |
|
|
|
17.
|
After the Revolutionary War, the National Government
a. | proved too weak to deal with growing economic and political
problems. | b. | refused to repay the war debt it owed to the States. | c. | permitted the States
to make agreements with foreign governments. | d. | began imposing harsh tax policies on property
owners and merchants. |
|
|
|
18.
|
In Benjamin Franklin's opinion, the final Constitution created by the
delegates can best be summarized as
a. | absolutely perfect. | b. | as near perfect as
possible. | c. | showing errors of opinion and self-interest. | d. | as full of
imperfections as those who assembled it. |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which of the following statements about the inauguration of George Washington as
the first U.S. president is NOT true?
a. | It followed his unanimous election in the Electoral College. | b. | It took place in New
York City, the country's temporary capital. | c. | It came after the ratification of the
Constitution. | d. | It followed Washington's appointment of James Madison as the first Vice
President. |
|
|
|
20.
|
A major objective of both the Annapolis Convention and the Philadelphia
Convention was to
a. | determine how the States should be represented in Congress. | b. | recommend a federal
plan for regulating interstate trade. | c. | raise an army for quelling incidents like
Shay's Rebellion. | d. | limit the growing power of the National
Government. |
|
|
|
21.
|
The government set up by the Articles of Confederation had
a. | no legislative or judicial branch. | b. | only a legislative and an executive
branch. | c. | only a legislative branch, consisting of a unicameral Congress. | d. | only a legislative
branch, consisting of a bicameral Congress. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which was an achievement of the Second Continental Congress?
a. | preparing a Declaration of Rights | b. | raising an American army | c. | establishing a
strong central government | d. | passing the Intolerable
Acts |
|
Essay
|
|
|
CRITICAL THINKING
|
|
|
23.
|
Providing Supporting Details Explain the objections that led Patrick
Henry to describe the Constitution as "the most fatal plan that could possibly be conceived to
enslave a free people."
|
|
|
24.
|
Determining Relevance How did the United States Constitution expand upon
the basic ideas about government that the colonists had developed up to the time of the
Constitutional Convention?
|
Other
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Distinguish between the terms in each pair
below.
|
|
|
25.
|
constitution/charter
|
|
|
26.
|
Framers/Federalists
|