Matching
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Match each item with the correct statement
below. You will not use all the terms. a. | amendment | b. | Bill of
Rights | c. | checks and balances | d. | constitutionalism | e. | article | f. | rule of law | g. | separation of
powers |
|
|
|
1.
|
A(n) ____ is a way to change the Constitution.
|
|
|
2.
|
The government and its officers must obey the ____, which is another way of
describing the concept of limited government.
|
|
|
3.
|
A(n) ____ is one of the seven numbered sections of the Constitution.
|
|
|
4.
|
The system of ____ helps keep one branch of government from dominating the
actions of the others.
|
|
|
5.
|
The Constitution provides for the ____ by creating three distinct branches of
government: legislative, executive, and judicial.
|
Other
|
|
|
IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS
Use each key term in a sentence that shows
the meaning of the term.
|
|
|
6.
|
|
|
|
7.
|
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
MAIN IDEAS
|
|
|
8.
|
With the words, "We the People," the Constitution establishes its
authority on the basis of
a. | popular sovereignty. | b. | the rule of law. | c. | the separation of
powers. | d. | limited government. |
|
|
|
9.
|
Which statement about the Bill of Rights is NOT true?
a. | The amendments arose from the controversy over ratification of the
Constitution. | b. | The amendments were ratified at the same time as the
Constitution. | c. | The amendments guarantee such basic rights as freedom of expression and fair and
equal treatment before the law. | d. | The amendments are the first ten of the
Constitution. |
|
|
|
10.
|
The informal amendment process
a. | involves changing the written words of the Constitution. | b. | has been used very
little in the past 200 years. | c. | can occur only with the approval of the
States. | d. | results from the daily experiences of government. |
|
|
|
11.
|
The President's Cabinet is an example of constitutional change by
a. | unwritten custom. | b. | court decision. | c. | State
action. | d. | basic legislation. |
|
|
|
12.
|
In most cases involving judicial review, the courts have
a. | had their decisions overturned by Congress. | b. | found the
governmental actions in question to be unconstitutional. | c. | found the
governmental actions in question to be constitutional. | d. | had their decisions vetoed by the
President. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Which of the following best describes the concept of limited government?
a. | Powers are divided among three independent branches of
government. | b. | All political power belongs to the people. | c. | Government must
operate within certain bounds set by the people. | d. | The people must behave according to rules set
by the government. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Which of the following is a method of formal amendment?
a. | proposal by three-fourths of the House of Representatives and ratification by
conventions in three-fourths of State legislatures | b. | proposal by two-thirds of the Senate and
ratification by two-thirds of State legislatures | c. | proposal by two-thirds of Congress and
ratification by three-fourths of State legislatures | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which of the following constitutional changes was a result of party
practices?
a. | the use of the electoral college as a "rubber stamp" for the popular
vote | b. | the revised structure of the federal court system | c. | executive
agreement | d. | the practice of senatorial courtesy |
|
|
|
16.
|
The basic constitutional rights of the people were FIRST set out in the
a. | 13th, 14th, and 15th amendments. | b. | 10th Amendment. | c. | Bill of
Rights. | d. | Equal Rights Amendment. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following is NOT true of the use of executive agreement?
a. | It extends the President's power. | b. | It carries the same legal force as a
treaty. | c. | It can be used to avoid the lengthy treaty-making process. | d. | It is among the
executive powers listed in Article II of the Constitution. |
|
|
|
18.
|
The legislative branch can check the judicial branch by its power to
a. | name federal judges. | b. | remove judges through
impeachment. | c. | declare executive actions unconstitutional. | d. | override a
presidential veto. |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which of the following is the subject of a constitutional amendment?
a. | the prohibition of alcohol | b. | repeal of a previous
amendment | c. | presidential term limits | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
20.
|
The Judiciary Act of 1789 was an example of
a. | a formal amendment to the Constitution. | b. | congressional change
to the Constitution. | c. | an executive agreement. | d. | a court
decision. |
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
INTERPRETING DIAGRAMSUse the diagram to answer the following
questions.
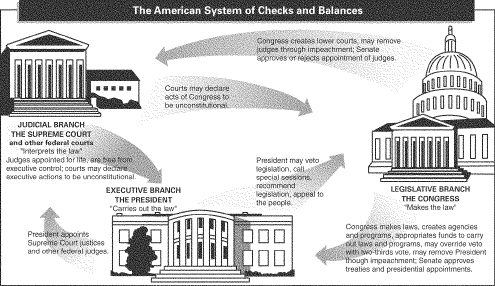
|
|
|
21.
|
Which branch of government can declare an act of Congress to be
unconstitutional?
|
|
|
22.
|
What powers do the President and Congress have over the appointment of Supreme
Court justices?
|
|
|
23.
|
Which branch of government can override a presidential veto?
|
Essay
|
|
|
CRITICAL THINKING
|
|
|
24.
|
Drawing Conclusions If a proposed amendment violates the Constitution,
should the Supreme Court be able to block its ratification? Explain.
|
|
|
25.
|
Determining Relevance How is the constitutional principle of federalism
reflected in the formal amendment process?
|