Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The Soviet Union dealt with uprisings in Poland, Hungary,
and Czechoslovakia during the 1950s and 1960s by
a. | taking over direct rule of these countries. | c. | permitting greater democratic reforms in government | b. | crushing the uprisings with military force. | d. | privatizing industrial
enterprises |
|
|
|
2.
|
What was the U.S. belief that if one country fell to communism, others would
follow?
a. | Domino Theory | c. | Theory of Relativity | b. | Blank Slate Theory | d. | Dominance
Theory |
|
|
|
3.
|
What was the purpose of the Truman Doctrine?
a. | to raise funds for Communist activities in Europe | c. | to judge political parties that
favored communism | b. | to create a Communist party in the United
States | d. | to support countries
that rejected communism |
|
|
|
4.
|
The main goal of the Marshall Plan was to
a. | Strengthen NATO forces in Western Europe | c. | Aid European recovery after
WWII | b. | Promote social justice | d. | Demand reparations from the Axis Powers |
|
|
|
5.
|
NATO was created in order to
a. | develop goodwill between Eastern and Western Europe.
| c. | facilitate regional economic development in North America.
| b. | encourage diplomatic solutions to regional problems in North
Africa. | d. | create a unified military defense between the U.S. and Western Europe.
|
|
|
|
6.
|
The Warsaw Pact was developed in 1955 as a response to
the
a. | formation of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization.
| c. | U.S. development of the hydrogen bomb. | b. | start of the Communist revolution in Cuba. | d. | UN intervention in Korea.
|
|
|
|
7.
|
The Soviet Union gave aid to newly developing nations during the 1960s in
order to gain
a. | new trade routes throughout Europe | c. | support for
democracy | b. | support for communism | d. | valuable natural resources |
|
|
|
8.
|
Use the following information to answer the question.
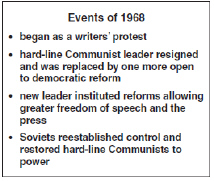 In what country did the events
being described above take place? In what country did the events
being described above take place?
a. | Czechoslovakia | c. | Hungary | b. | Yugoslavia | d. | Poland |
|
|
|
9.
|
What was the central reason for the success of Soviet satellite independence
movements?
a. | the formation of the European Union | c. | the emergence of strong Marxist
leaders. | b. | the development of new communication technologies | d. | The failure of Soviet economic, political, and
social policies. |
|
|
|
10.
|
What Cold War policy led to U.S. involvement in Korea?
a. | appeasement | c. | containment | b. | imperialism | d. | brinkmanship |
|
|
|
11.
|
The 1956 Suez Crisis began when
a. | the United States refused to give up control of the Suez Canal. | c. | Great Britain
refused to make improvements to the Suez Canal | b. | the Soviet Union bombed the Suez
Canal. | d. | Egypt seized control
of the Suez Canal. |
|
|
|
12.
|
What was one major goal of the Soviet Union during the
early years of the Cold War?
a. | to establish a competitive market economy | c. | to expand individual liberties in the Baltic republics | b. | to create a defensive buffer zone in Eastern Europe | d. | to attract foreign economic
investments |
|
|
|
13.
|
U.S. intervention in
Vietnam came as a result of the Cold War policy of a. | détente | c. | appeasement | b. | brinkmanship | d. | containment |
|
|
|
14.
|
Use the information below to complete the statement that
follows. 
This quote from a speech delivered
in 1947 forms part of the rationale for the
a. | Monroe Doctrine | c. | Truman Doctrine | b. | New Frontier | d. | Good Neighbor
Policy |
|
|
|
15.
|
Which of these is the main reason that Poland,
Czechoslovakia, Hungary, and Romania became satellites of the Soviet Union?
a. | These areas were given to the Soviet Union by a League of Nations
mandate | c. | The Soviet army occupied these areas at the end of World War II. | b. | The people in each
country voted in free elections to ally with the Soviets | d. | Hitler surrendered control of these areas to
the Soviet Union at the ened of the war. |
|
|
|
16.
|
What crisis brought the Soviet Union and the United
States to the brink of nuclear war in 1962?
a. | an attempt by leaders in communist Hungary to withdraw from the
Warsaw Pact | c. | an invasion of South Korea by armed communist forces from North
Korea | b. | the creation of East Germany as a separate Soviet military
occupation zone | d. | the installation in Cuba of Soviet offensive intermediate-range
missiles |
|
|
|
17.
|
When the United States sent military aid to Chinese
nationalists to help them resist communism, it was continuing a foreign policy first asserted in the
a. | Marshall Plan | c. | Truman Doctrine | b. | Potsdam Agreement | d. | Teheran
Conference |
|
|
|
18.
|
The Great Leap Forward reflected China’s desire to
a. | build a People’s Army | c. | collectivize
agriculture. | b. | end Western investment | d. | struggle against
imperialism |
|
|
|
19.
|
One of the major goals of China's Cultural Revolution was
__________.
a. | establishing a society in which both the workers and the intellectuals were
equal | c. | establishing a society in which the intellectuals were glorified while the workers
were persecuted | b. | establishing a society in which the workers were glorified while the intellectuals
were persecuted | d. | establishing a society in which artistic pursuits were
glorified |
|
|
|
20.
|
What was the primary goal of the uprising on Poland, Hungary, and
Czechoslovakia during the 1950s and 1960s?
a. | stopping the genocide of minority groups. | c. | desire to join
NATO | b. | freedom from Soviet control | d. | reestablishing the Orthodox Church |
|
|
|
21.
|
In the 1940s and 1950s, what did the region described as being “behind
the iron curtain” include?
a. | Soviet Union only | c. | democratic nations of Western Europe | b. | Soviet Union and its
satellite nations | d. | East
Germany only |
|
|
|
22.
|
The component of the United Nations that provides a forum for all member
nations is the
a. | Security Council. | c. | Secretary-General | b. | Secretariat | d. | General
Assembly |
|
|
|
23.
|
Which two groups fought a civil war in China both before and after World War
II?
a. | the peasants and the middle class | c. | the Nationalists and the
Communists | b. | the warlords and the emperor | d. | the Socialists and the
Nationalists |
|
|
|
24.
|
Which of the following was a primary cause of the Cold
War between the United States and the Soviet Union?
a. | a competition for political influence over other coutnries | c. | a deep reduction in
military expenditures | b. | direct, armed conflict between the two
nations | d. | the founding of the
United Nations |
|
|
|
25.
|
After World War II, Western Europe became united in its opposition to
a. | Germany’s rising power. | c. | a military alliance with the United
States. | b. | investment in foreign markets. | d. | the spread of communism.
|
|
|
|
26.
|
Which country’s solidarity union movment of the 1980s became the main
force of opposition to communist rule?
a. | East Germany | c. | Romania | b. | Poland | d. | Ukraine |
|
|
|
27.
|
“The most important problem does not lie
in understanding the laws of the objective world and thus being able to explain it, but in applying
the knowledge of these laws actively to change the world.”
—from Selected Works, Vol I,
Mao Tse-Tung
The quotation above reflects Mao
Tse-Tung’s commitment to
a. | capitalism | c. | science | b. | education | d. | revolutionary action
|
|
|
|
28.
|
The Soviet Union was able to take control in Eastern Europe following World
War II because
a. | The Chinese-Soviet alliance increased its military strength. | c. | Soviet troops were
already stationed in Eastern Europe during the war. | b. | The Soviet Union
offered jobs to impoverished Eastern Europeans. | d. | U.S. President Roosevelt died
before the war ended, voiding old treaties.
|
|
|
|
29.
|
What the USSR’s response to the military alliance of the
West?
a. | Nazi-Soviet Pact | c. | Warsaw Pact | b. | Peristroika | d. | NATO |
|
|
|
30.
|
What was
one outcome of World War II? a. | England and France increased their overseas colonial
possessions. | c. | Japan and Germany became dominant military powers in their
regions. | b. | The communists gained control over most of Western Europe.
| d. | The Soviet Union emerged as an international superpower
|
|
|
|
31.
|
Under which program did Gorbachev attempt to modify the economic structure of
the Soviet economy by allowing some private enterprise?
a. | glasnot | c. | perestroika | b. | shock therapy | d. | modernization |
|
|
|
32.
|
Which of the following was not a cause of the Cuban Missile
Crisis?
a. | US policy to prevent the spread of Communism | c. | The proliferation of nuclear
weapons | b. | Soviet desire to support communist allies | d. | The suppression of free elections in
Cuba. |
|
|
|
33.
|
The United States entered the Vietnam War to
a. | disarm the South Vietnam government | c. | achieve “peace without
victory” | b. | stop the spread of communism into Southeast Asia | d. | take the first step in an effort to imperialize
the entire planet |
|
Matching
|
|
|
Match each term with the correct description. a. | domino theory | d. | Berlin Wall | b. | containment | e. | brinkmanship | c. | iron
curtain |
|
|
|
34.
|
The idea that if a nation falls under Communist control, nearby nations will
also fall under Communist control
|
|
|
35.
|
An actual wall separating East Berlin from West Berlin.
|
|
|
36.
|
The willingness to go to the brink of war to force the other side to back
down
|
|
|
37.
|
During the Cold War, the boundary separating the Communist nations of Eastern
Europe from the mostly democratic nations of Western Europe.
|
|
|
38.
|
The policy of preventing the spread of Communism
|
|
|
Match each term with the correct definition. a. | detente | d. | Warsaw Pact | b. | Marshall Plan | e. | NATO | c. | perestroika |
|
|
|
39.
|
A U.S. program of economic aid to European countries to help them rebuild after
World War II
|
|
|
40.
|
A policy of reducing Cold War tensions
|
|
|
41.
|
A restructuring of the Soviet economy to permit more local decision making,
begun by Mikhail Gorbachev in 1982
|
|
|
42.
|
A defensive military alliance formed in 1949 that includes Western European
nations and the United States
|
|
|
43.
|
A military alliance formed in 1955 by the Soviet Union and several Eastern
European nations
|